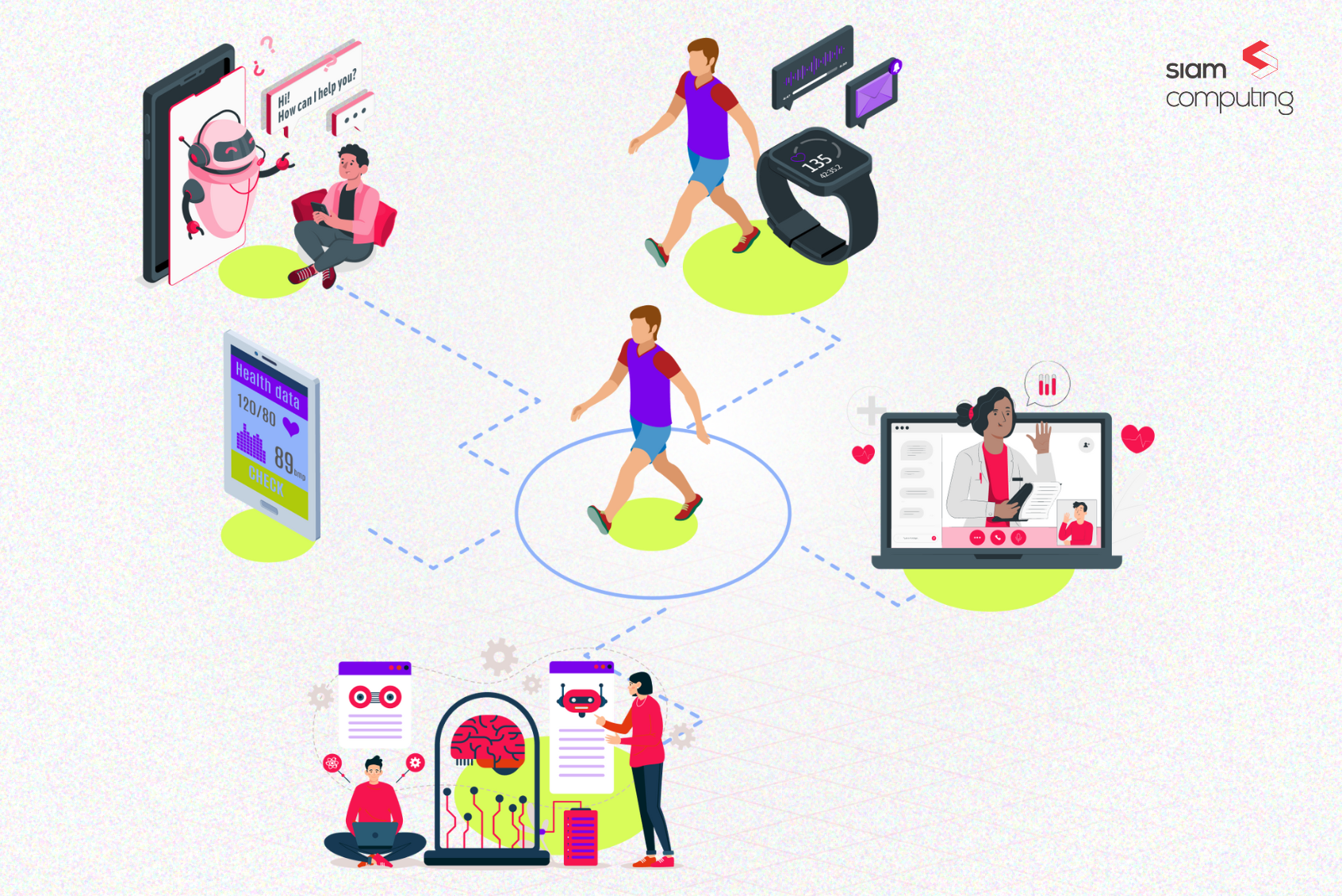
Imagine a doctor urgently needing a patient’s medical history to make a critical decision, but instead of getting the records instantly, they are stuck waiting. This scenario isn’t just frustrating—it’s dangerous. In healthcare, time isn’t just money; it can mean the difference between life and death.
Relatedly, quick access to accurate medical records is not just a convenience—it’s a necessity. The ability to retrieve medical records swiftly can significantly impact patient outcomes, streamline care delivery, and reduce costs, especially within the context of value-based care.
However, achieving quick turnaround times in medical record retrieval is fraught with challenges. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of medical record retrieval, explore the various types of medical records, discuss why speed is crucial in today’s value-based care environment, and look at the stakeholders who need these records most.
Finally, we’ll explore the nuanced, often overlooked issues that make this process so complex, and how innovative technology and streamlined processes can make a real difference.
Types of Medical Records
Here are a few common types of medical records that are involved in day-to-day operations of healthcare providers and payers.
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs): Digital versions of patients’ paper charts, EHRs are real-time, patient-centered records that make information available instantly and securely to authorized users.
- Electronic Medical Records (EMRs): A narrower view of a patient’s medical history, usually within one practice, EMRs are a digital version of the paper charts in a clinician’s office.
- Personal Health Records (PHRs): Health records maintained by patients themselves, providing a complete summary of their health from multiple providers.
- Radiology Reports: Documents that describe the results of imaging studies such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs.
- Pathology Reports: Detailed reports that describe the diagnosis determined from the examination of cells and tissues.
- Laboratory Reports: Records of the results of laboratory tests, including blood tests, urinalysis, and biopsies.
- Discharge Summaries: Summaries of a patient’s hospital stay, including the reasons for admission, findings, treatment, and instructions for follow-up care.
- Operative Reports: Detailed reports about surgical procedures, including the methods and outcomes.
- Progress Notes: Daily updates on a patient’s condition by healthcare providers during a hospital stay.
- Consultation Reports: Specialist reports following consultations, including diagnoses and treatment recommendations.
The Importance of Speed in the Value-Based Care Landscape
In the shift from fee-for-service to value-based care, the speed of medical record retrieval has become increasingly critical. Value-based care models reward healthcare providers for the quality rather than the quantity of care. Timely access to comprehensive medical records enables providers to make informed decisions quickly, reduce redundant testing, and avoid potential complications—all of which contribute to improved patient outcomes and cost savings.
For instance, in an emergency department, a delay in retrieving a patient’s medical history could lead to unnecessary tests or inappropriate treatment, potentially resulting in harm to the patient and higher costs. Conversely, quick access to the necessary records can facilitate early diagnosis and intervention, aligning with the goals of value-based care.
Delays in retrieving medical records can have far-reaching consequences across the healthcare ecosystem:
Increased Costs: Delays can lead to prolonged hospital stays, unnecessary tests, and repeated procedures, all of which drive up healthcare costs.
Compromised Care Quality: Without timely access to patient records, healthcare providers may miss critical information, leading to suboptimal treatment decisions.
Billing and Reimbursement Issues: Slow TaT in record retrieval can result in delayed or denied insurance claims, disrupting cash flow for providers and leading to patient dissatisfaction.
Regulatory Compliance Risks: Healthcare organizations are bound by regulations such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the U.S., which mandate timely access to patient records. Non-compliance can result in hefty fines and reputational damage.
Stakeholders and Their Perspectives
The need for quick TaT in medical record retrieval is recognized by various stakeholders, each with their unique challenges and priorities.
1. Healthcare Payers
For payers, the efficient processing of claims is a top priority. They rely on accurate and complete medical records to validate claims and reimburse providers accordingly. Delays in record retrieval can lead to bottlenecks in the claims process, resulting in higher administrative costs and potential disputes with providers. Moreover, in a VBC model, payers are increasingly focused on ensuring that the care provided aligns with the value metrics set forth in their contracts with providers. Quick access to medical records enables payers to verify that care was delivered in a cost-effective manner that meets quality benchmarks.
Challenges:
- Data Accuracy: Incomplete or outdated records can lead to claim denials or incorrect reimbursements.
- Administrative Burden: Manual retrieval processes are time-consuming and error-prone, leading to inefficiencies.
- Regulatory Compliance: Payers must ensure that the retrieval process complies with legal requirements to protect patient privacy.
Solutions:
- Automation and AI: Leveraging automation and artificial intelligence can streamline the record retrieval process, reducing the time and effort required.
- Standardization of Records: Implementing standardized formats for medical records can facilitate quicker retrieval and processing.
- Interoperability: Enhancing data interoperability between different Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems can significantly improve TaT.
2. Healthcare Providers
Providers are on the frontlines of patient care, and they need quick access to medical records to deliver timely and effective treatment. Delays in accessing records can disrupt the continuity of care, leading to poor patient outcomes and increased liability risks. Moreover, in a VBC model, providers are accountable for the quality and efficiency of the care they deliver. Quick TaT in record retrieval allows providers to meet these expectations, avoid redundant testing, and focus on preventive care.
Challenges:
- Data Silos: Patient data is often stored in disparate systems, making it difficult to retrieve records quickly.
- Resource Constraints: Providers may lack the resources or expertise to manage record retrieval efficiently, especially in smaller practices.
- Patient Privacy Concerns: Providers must navigate complex regulations to ensure that patient records are retrieved securely and confidentially.
Solutions:
- Integrated EHR Systems: Implementing integrated EHR systems can reduce the time required to access patient records across different departments or facilities.
- Outsourcing: Providers can partner with specialized vendors to manage the record retrieval process, ensuring quick TaT without burdening in-house staff.
- Patient Portals: Encouraging patients to use digital portals to upload and share their records can reduce the reliance on manual retrieval processes.
3. Patients
In the VBC landscape, patients are at the center of care delivery. They benefit directly from quick TaT in medical record retrieval, as it leads to more coordinated and efficient care. Timely access to their records empowers patients to be more involved in their care decisions and improves their overall healthcare experience. Additionally, quick TaT reduces the risk of errors, misdiagnoses, and unnecessary treatments, all of which can compromise patient safety.
Challenges:
- Accessibility: Patients may face difficulties in accessing their records, especially if they are stored across multiple healthcare providers.
- Understanding: Patients may struggle to understand the importance of quick TaT and how it affects their care.
- Trust: Concerns about data privacy and security can make patients hesitant to share their medical records electronically.
Solutions:
- Patient Education: Educating patients about the benefits of quick TaT and how to access their records can enhance their engagement in the care process.
- Simplified Access: Healthcare providers can offer user-friendly patient portals that make it easy for patients to access and share their records.
- Transparency: Providers and payers should communicate clearly with patients about how their data is being used and protected, building trust in the system.
The Technical Challenges in Achieving Quick TaT
Achieving quick TaT in medical record retrieval is not without its technical challenges. The healthcare industry is plagued by data fragmentation, interoperability issues, and varying levels of technology adoption across providers. Here’s a closer look at the technical hurdles that need to be addressed:
1. Data Fragmentation and Silos
Medical records are often fragmented across multiple systems, including EHRs, paper records, and third-party applications. These silos create significant barriers to quick retrieval, as data must be aggregated and normalized from disparate sources.
Solution:
- Health Information Exchanges (HIEs): Establishing or participating in HIEs can facilitate data sharing across providers and payers, reducing fragmentation and improving TaT.
- Data Integration Platforms: Utilizing data integration platforms can help aggregate and harmonize data from various sources, providing a unified view of patient records.
2. Interoperability Issues
Interoperability—the ability of different IT systems and software applications to communicate and exchange data—remains a significant challenge in healthcare. Inconsistent data formats, lack of standardized protocols, and varying levels of system sophistication can all contribute to delays in medical record retrieval.
Solution:
- Adoption of Standards: Implementing and adhering to interoperability standards, such as HL7 FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources), can streamline data exchange and retrieval.
- APIs for Data Exchange: Leveraging APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) can enable real-time data sharing between systems, reducing retrieval time.
3. Legacy Systems and Technology Gaps
Many healthcare organizations still rely on outdated legacy systems that are not designed for the rapid retrieval and sharing of digital medical records. These systems often lack the capabilities needed to support the demands of VBC.
Solution:
- System Modernization: Investing in the modernization of IT infrastructure is crucial to improving TaT. This includes upgrading EHR systems, adopting cloud-based solutions, and implementing advanced analytics.
- Vendor Partnerships: Partnering with technology vendors that specialize in healthcare IT can help bridge the gap between legacy systems and modern requirements.
4. Security and Compliance Considerations
The need to comply with stringent data protection regulations, such as HIPAA, adds another layer of complexity to medical record retrieval. Ensuring that records are retrieved quickly without compromising security or violating compliance requirements is a delicate balance.
Solution:
- Data Encryption: Ensuring that all data is encrypted both in transit and at rest can protect patient information during the retrieval process.
- Access Controls: Implementing robust access controls and auditing mechanisms can help maintain compliance while facilitating quick TaT.
- Training: Regularly training staff on compliance and security best practices can reduce the risk of breaches and ensure that retrieval processes are followed correctly.
Innovations Shaping the Future of Medical Record Retrieval
As the healthcare industry continues to evolve, so too will the methods and technologies used to retrieve medical records. Several emerging trends and innovations hold the potential to further improve TaT in medical record retrieval.
1. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are poised to revolutionize medical record retrieval by automating data extraction, categorization, and analysis. These technologies can identify patterns and correlations within medical records that may not be immediately apparent to human reviewers, speeding up the retrieval process and enhancing accuracy.
2. Blockchain Technology
Blockchain offers a decentralized and secure way to store and share medical records. By creating a tamper-proof digital ledger, blockchain can ensure that records are retrieved quickly and securely, with a clear audit trail.
3. Telemedicine Integration
The rise of telemedicine has highlighted the need for quick TaT in medical record retrieval. As telemedicine becomes more integrated into routine care, seamless access to patient records will be essential to provide timely and effective remote care.
4. Patient-Driven Data Portability
With the growing emphasis on patient-centered care, there is a push towards empowering patients to control and share their medical records as they see fit. Innovations in data portability, such as digital health wallets and portable health records, will enable patients to facilitate quick TaT by directly sharing their data with providers and payers.
Build Better Healthcare Systems with Siam
In the Value-Based Care landscape, quick Turnaround Time in medical record retrieval is not just a nice-to-have—it’s a critical necessity. While challenges remain, from data fragmentation to interoperability issues, the adoption of modern technologies and best practices can significantly improve TaT, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes and a more sustainable healthcare system.
If you’re facing challenges in optimizing Turnaround Time for medical record retrieval or looking to implement cutting-edge solutions to enhance your Value-Based Care strategy from a technological and strategic operations perspective, Siam Computing can help.
Contact our team of expert product strategists who specialize in developing customized, scalable solutions tailored to the unique needs of healthcare payers and providers. Let’s explore how we can collaborate to build the next generation of healthcare products that drive efficiency, improve patient outcomes, and ensure compliance.