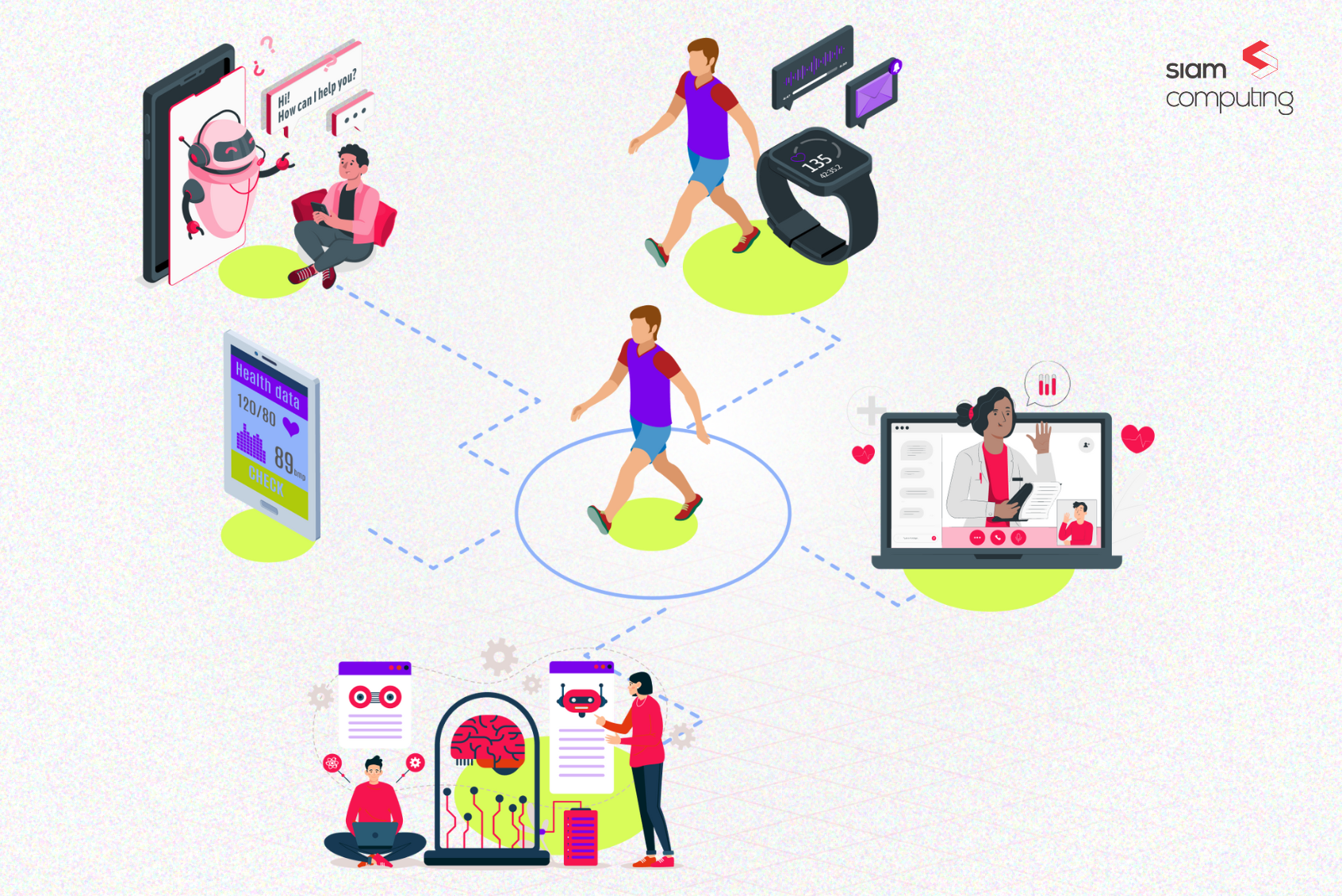
One of the key drivers of modernization in healthcare diagnosis and preventive care, is the influx of data generated by patients outside traditional clinical settings. This data, known as Patient-Generated Health Data (PGHD), includes health-related information collected by patients themselves, often via wearable devices, mobile apps, and home health monitoring tools.
The integration of PGHD into Electronic Health Records (EHRs) is crucial for enhancing care delivery, improving outcomes, and reducing healthcare costs.
In this article, we explore the technical challenges associated with integrating PGHD into EHRs, solutions to these challenges, best practices, and how this integration can enhance care delivery for payers and providers, while improving patient outcomes.
Understanding PGHD and Its Potential
PGHD encompasses a wide range of data types, including but not limited to:
- Vital signs (e.g., blood pressure, heart rate)
- Fitness metrics (e.g., steps taken, calories burned)
- Symptom tracking (e.g., pain levels, medication side effects)
- Behavioral data (e.g., sleep patterns, diet, physical activity)
- Device data from wearables (e.g., glucose monitors, smartwatches)
Integrating these data streams into EHRs provides a more holistic view of a patient’s health, beyond the traditional episodic care delivered in clinical settings.
This integration helps healthcare providers and payers develop a comprehensive approach to care, enabling more personalized and proactive interventions, reducing hospital readmissions, and improving the quality of care.
Enhancing Care Delivery for Payers and Providers
For payers, PGHD offers a valuable tool for reducing costs and improving the quality of care. By monitoring patient data in real-time, payers can incentivize preventive care and early interventions, avoiding costly complications. For example, real-time monitoring of chronic conditions like heart disease or diabetes allows payers to identify patients at risk of hospitalization and provide timely interventions.
For providers, PGHD offers a way to deliver more personalized and proactive care. Providers can monitor patient progress between visits, adjust treatment plans based on real-time data, and engage patients in shared decision-making. This continuous monitoring is particularly useful for managing chronic conditions, where real-time data can provide early warning signs of deterioration.
Here are the key benefits of PGHD Integration
1. Enhanced Care Coordination
Integrating PGHD into EHRs creates a seamless flow of information between patients, providers, and payers. This integration improves care coordination across different settings, ensuring that all stakeholders have access to a complete picture of a patient’s health.
2. Improved Patient Engagement
When patients actively contribute to their healthcare data, they become more engaged in their care. PGHD can facilitate patient-driven decision-making, improve adherence to treatment plans, and promote better self-management of chronic conditions.
3. Personalized Care Delivery
PGHD allows providers to tailor treatments and interventions to individual patients based on real-time data. For example, patients with diabetes can benefit from continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) data integrated into their EHR, enabling providers to adjust medications and treatment plans dynamically.
4. Cost Reduction
For payers, PGHD integration can reduce unnecessary hospital admissions, emergency room visits, and healthcare expenditures. By using continuous data to monitor high-risk patients, payers can intervene early and prevent costly medical complications.
Technical Challenges of Integrating PGHD into EHRs
While the benefits of PGHD are clear, integrating it into EHRs presents several technical challenges. Let’s dive into these key issues.
1. Data Standardization and Interoperability
PGHD comes from various sources, such as mobile health apps, wearable devices, and home monitoring tools. Each source may use different data formats and standards, leading to inconsistencies when integrating with EHRs. Achieving interoperability between systems and devices is essential for ensuring data can be transmitted, received, and understood by EHR systems.
2. Data Overload
Healthcare providers are already burdened with vast amounts of data from traditional EHR systems. The influx of additional PGHD can contribute to data overload, making it difficult for providers to sift through irrelevant or low-quality data and identify actionable insights.
3. Data Security and Privacy
The integration of PGHD into EHRs raises concerns about patient privacy and data security. PGHD is often collected on consumer-grade devices that may not meet healthcare security standards. Ensuring compliance with regulations like HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) is critical to maintaining patient trust and safeguarding sensitive health information.
4. Data Accuracy and Validation
Since PGHD is generated by patients, there is a risk that the data may be inaccurate or incomplete. Devices used to collect PGHD may not have the same level of precision as clinical equipment, and patients may misreport symptoms or forget to log critical information.
5. Integration with Clinical Workflows
EHR systems were not initially designed to accommodate PGHD, and integrating this data into clinical workflows can be disruptive. Providers may face challenges in effectively incorporating PGHD into their decision-making processes, especially if the data is not presented in a user-friendly format or integrated seamlessly with existing systems.
Solutions to Overcome Technical Challenges
To address these challenges, healthcare organizations must adopt a strategic and structured approach. Here are some solutions:
1. Adoption of Standardized Data Formats
To improve interoperability, industry-wide adoption of standardized data formats, such as Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) and Health Level Seven (HL7), is essential. These standards provide a common framework for exchanging healthcare information, enabling data from wearables, apps, and other sources to be easily integrated into EHRs.
2. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML can help sift through large volumes of PGHD to identify patterns and insights that are relevant to patient care. These technologies can filter out low-value data, flagging only critical information for provider review. Additionally, AI can provide predictive analytics to identify patients at risk for specific conditions or complications.
3. Robust Security Protocols
Ensuring the privacy and security of PGHD requires robust encryption, secure data transmission protocols, and compliance with regulations such as HIPAA. Healthcare organizations must conduct thorough risk assessments and implement security measures such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), data anonymization, and access controls to protect sensitive patient data.
4. Data Validation Mechanisms
To address concerns about data accuracy, healthcare organizations should implement data validation mechanisms. These may include cross-referencing PGHD with clinical data from the EHR or using device-specific calibration tools to ensure that data from consumer devices is reliable.
5. Integration with Clinical Decision Support (CDS) Tools
Integrating PGHD with clinical decision support (CDS) tools can streamline workflows by presenting data in a way that is actionable for providers. CDS systems can flag relevant PGHD, generate alerts for abnormal readings, and provide recommendations based on patient-specific data. This ensures that providers receive only the information they need, reducing data overload.
Best Practices for Integrating PGHD into EHRs
The successful integration of PGHD into EHRs requires careful planning and adherence to best practices. Here are some key strategies to consider:
1. Collaborate with Patients
Since PGHD is patient-generated, healthcare organizations should actively engage patients in the data collection process. Providing education on the importance of PGHD, how to use monitoring devices, and ensuring patient-friendly interfaces will empower patients to take an active role in their care.
2. Pilot Programs and Incremental Implementation
Rather than rolling out PGHD integration across an entire organization at once, healthcare providers should implement pilot programs to test the feasibility and impact of integration. Starting with a small group of patients or focusing on specific chronic conditions (e.g., diabetes, hypertension) can provide valuable insights and allow for iterative improvements.
3. Cross-Functional Collaboration
Successful PGHD integration requires collaboration between various stakeholders, including IT teams, clinical staff, payers, and patients. Involving all relevant parties ensures that technical, clinical, and operational considerations are addressed, and the system is designed to meet the needs of all users.
4. Focus on User-Centered Design
When designing EHR interfaces for PGHD integration, it’s essential to focus on user-centered design principles. The user interface should be intuitive and provide clinicians with easy access to actionable data. Visualization tools, such as trend charts or graphs, can help providers quickly assess changes in a patient’s health status.
5. Evaluate and Iterate
Healthcare organizations should continuously evaluate the effectiveness of PGHD integration. By gathering feedback from providers and patients, conducting regular audits of data accuracy, and assessing clinical outcomes, organizations can refine their systems to ensure that PGHD is being used to its full potential.
Impact on Patient Outcomes
The ultimate goal of integrating PGHD into EHRs is to improve patient outcomes. Here’s how this integration can drive better health results:
- Timely Interventions: Continuous monitoring of patients’ health allows providers to identify issues early, leading to timely interventions that can prevent complications and hospitalizations.
- Chronic Disease Management: PGHD enables better management of chronic diseases by providing insights into patient behavior, treatment adherence, and disease progression outside the clinical setting.
- Increased Engagement: When patients see their data being used in real-time to make informed decisions, they are more likely to adhere to treatment plans and take an active role in managing their health.
- Personalized Care: Real-time data allows providers to tailor care plans to individual patient needs, improving the overall quality of care and patient satisfaction.
How Siam Computing Can Help
Integrating PGHD into EHRs represents a significant opportunity for healthcare organizations to improve care delivery, reduce costs, and enhance patient outcomes. Despite the technical challenges and ethical considerations associated with collecting and using PGHD, solutions such as data standardization, AI-driven analytics, and robust security measures can help overcome these hurdles.
At Siam Computing, we specialize in building secure digital healthcare solutions and patient experience platforms tailored to the unique needs of healthtech startups, hospitals, and other healthcare institutions. Our expertise in developing custom healthcare solutions enables us to effectively leverage PGHD to improve patient care and outcomes.
If you are interested in leveraging Patient-Generated Health Data to enhance your healthcare digital products and platforms, contact our product strategists today. Learn how our digital healthcare experts can help you develop custom solutions that effectively collect, analyze, and utilize PGHD to improve patient care, engagement, and outcomes.