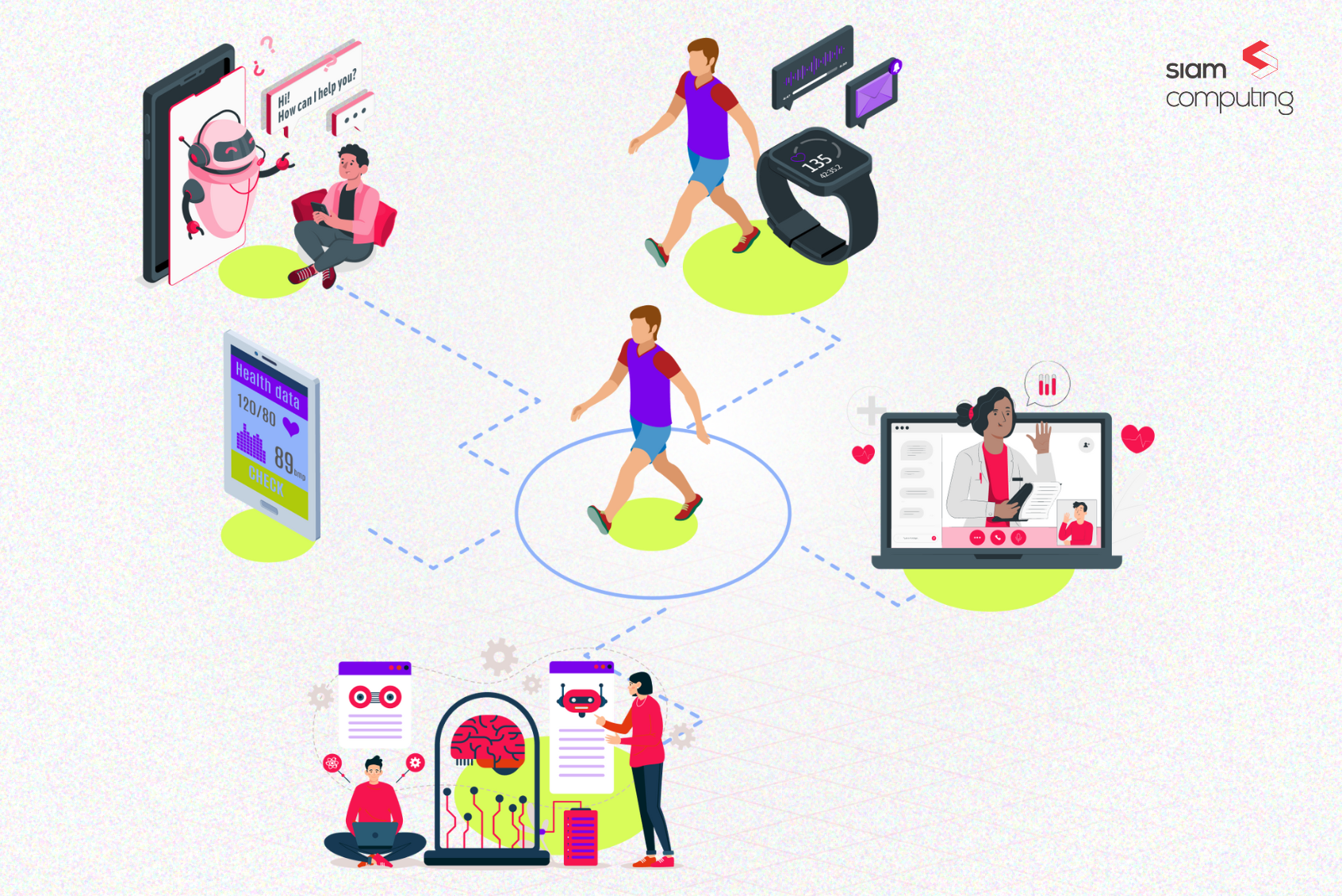
Imagine a world where healthcare providers have access to real-time, comprehensive data about their patient’s health and wellness, allowing them to deliver personalized and proactive care that goes beyond traditional medical visits. This is not a distant reality but a promising future enabled by Patient-Generated Health Data (PGHD).
PGHD is revolutionizing the healthcare industry by empowering patients, enhancing clinical decision-making, and contributing to the development of personalized medicine.
But, what exactly is Patient Generated Health Data?
Patient Generated Health Data (PGHD) refers to the data collected, recorded, and shared by patients or their family members and caregivers, about the patient’s health and wellness. This can include a wide range of information, such as biometric data, symptoms, medication adherence, diet and nutrition, physical activity, sleep patterns, and more.
PGHD is typically collected through various digital health tools and platforms, including wearable devices, mobile apps, patient portals, and telehealth services.
How does PGHD enhance healthcare delivery?
Patient generated health data can provide a more comprehensive picture of ongoing patient health. It fills the gaps in existing clinical data with information about how patients are doing between medical visits, helping care providers better understand patient health.
By doing so, PGHD enables shared decision-making about preventive and chronic care management. It also offers potential cost savings and improvements in quality, care coordination, and patient safety.
PGHD is distinct from data generated in clinical settings because the patients, and NOT providers, are primarily responsible for capturing or recording these data. So the patients have more control over how to share these data to healthcare providers and others.
Sources of PGHD and data types
The cornerstone of PGHD lies in the diverse sources from which it originates. These sources empower patients to actively participate in their healthcare journey, meticulously recording valuable data points that paint a comprehensive picture of their well-being.
Let’s delve into the wellsprings of this rich data, highlighting the specific types of PGHD each source contributes:
Wearable Devices
These ubiquitous IoMT companions have become an extension of ourselves, constantly monitoring and capturing a wealth of data on our physical well-being. Smartwatches, smart rings, and fitness trackers are a few examples of these tireless data collectors.
They provide insights into a wide array of data, including:
- Biometric Data: Heart rate, blood oxygen levels, and body temperature are just some of the biometric data points continuously monitored by wearables. This real-time information can reveal potential health issues and inform timely interventions.
- Activity Levels: Steps taken, distance covered, and calories burned – wearables provide a detailed picture of our daily physical activity. This data is crucial for understanding our fitness levels, identifying sedentary behavior, and motivating us to move more.
- Sleep Patterns: Sleep duration, quality, and sleep stages – these insights can be gleaned from sleep tracking features on wearables. By revealing sleep disturbances and potential underlying health issues, this data empowers us to prioritize sleep hygiene for optimal health.
Mobile Health (mHealth) Applications:
The proliferation of mHealth apps has transformed smartphones into powerful tools for health management. These apps empower patients to actively track and manage their health, capturing a diverse range of PGHD.
- Symptom and Condition Tracking: From headaches and fatigue to mood swings and pain levels, patients can log their symptoms, severity, and duration within mHealth apps. This data provides valuable insights for diagnosis, treatment monitoring, and understanding the impact of a condition on daily life.
- Medication Adherence and Management: Medication tracking apps ensure patients stick to their prescribed regimens by sending reminders and logging medication intake, dosage, and timing. This data can help healthcare providers identify medication adherence issues and adjust treatment plans as necessary.
- Diet and Nutrition: Food and calorie tracking apps allow patients to monitor their dietary intake, promoting healthier eating habits and weight management. This data can reveal dietary patterns, identify areas for improvement, and support personalized nutrition plans.
Patient Portals:
Secure online platforms offered by healthcare providers allow patients to become more informed participants in their healthcare. Beyond accessing medical records and scheduling appointments, these portals facilitate the collection and tracking of patient-reported outcomes (PROs).
- Health and Wellness Goals: Setting and tracking goals related to weight management, smoking cessation, or physical activity levels empowers patients to take ownership of their health journey. Patient portals can capture data on progress towards these goals and provide motivational support.
- Patient-Reported Outcomes (PROs): Quality of life assessments and surveys conducted through patient portals provide crucial insights into a patient’s subjective experience of their health and well-being. This data goes beyond physical parameters and allows healthcare providers to understand how a condition affects a patient’s daily activities and mental well-being.
- Lifestyle Data: Patient portals can be used to collect data on various lifestyle factors like smoking habits, alcohol consumption, and stress levels. This data can help identify potential risk factors for chronic diseases and inform preventative care strategies.
Home Monitoring Devices
Beyond wearables, a growing array of home monitoring devices empowers patients to track specific health parameters, providing crucial biometric data:
- Blood Pressure Monitors: Regular blood pressure readings taken at home using these devices provide valuable data for managing hypertension and cardiovascular health. This data allows for early detection of potential issues and timely intervention.
- Glucose Meters: For diabetic patients, blood glucose monitoring devices enable close tracking of blood sugar levels. This data is essential for effective diabetes management and medication adjustments.
- Pulse Oximeters: These devices measure blood oxygen saturation, providing insights into potential respiratory issues. By monitoring blood oxygen levels at home, patients can identify early signs of problems and seek medical attention as needed.
This rich tapestry of PGHD sources, each contributing unique data points, empowers patients to become active participants in their healthcare. By harnessing the power of these diverse sources, healthcare providers can gain a more comprehensive understanding of a patient’s health, leading to improved diagnosis, treatment, and preventative care strategies.
Importance of PGHD in Healthcare
The collection and analysis of PGHD can play a crucial role in enhancing patient engagement, improving clinical decision-making, and contributing to the development of personalized medicine.
Enhancing Patient Engagement
One of the significant benefits of PGHD is its ability to empower patients to take an active role in their healthcare. By providing patients with access to their health data, they can gain a better understanding of their health status, monitor their progress over time, and make informed decisions about their care.
Improving Clinical Decision-Making
PGHD can provide clinicians with a more comprehensive view of a patient’s health, beyond what is captured during regular medical visits. This additional data can help clinicians identify patterns, trends, and potential health issues more effectively, leading to more personalized and timely interventions.
Personalized Medicine and treatment plan
With the advent of precision medicine, the ability to tailor medical treatments and interventions to individual patients has become increasingly important. PGHD can contribute to the development of personalized treatment plans by providing clinicians with valuable insights into a patient’s real-time health and unique health profile, preferences, and needs.
Challenges and Considerations in Using PGHD
While PGHD holds significant promise, there are several challenges and considerations that healthcare providers and organizations must address to effectively leverage this valuable data.
Data Accuracy and Reliability
Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of PGHD is crucial for its successful use in healthcare. Issues such as inaccurate data entry, device malfunctions, and user error can lead to unreliable data, which can negatively impact clinical decision-making and patient care.
Data Privacy and Security
Protecting the privacy and security of sensitive patient information is paramount when collecting, storing, and sharing PGHD. Healthcare organizations must implement robust data protection measures and comply with relevant data privacy regulations, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States.
Integration with Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
Integrating PGHD into existing Electronic Health Records (EHRs) can be challenging due to differences in data formats, standards, and interoperability issues. Healthcare organizations need to invest in interoperable systems and technologies that enable seamless integration and sharing of PGHD across different healthcare platforms and providers.
Future Trends in PGHD
The future of PGHD in healthcare is promising, with ongoing advancements in technology, artificial intelligence (AI), and data analytics poised to further revolutionize the collection, analysis, and utilization of PGHD.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning technologies can analyze large volumes of PGHD to identify patterns, trends, and insights that may not be apparent to clinicians. These advanced analytics can help predict and prevent potential health issues, optimize treatment plans, and improve patient outcomes.
Interoperability and Standardization
Global efforts to standardize and integrate PGHD across different healthcare systems and platforms are underway to improve interoperability and data exchange. Initiatives such as Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) in the West and India’s Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM) aim to establish common standards and frameworks for sharing and integrating PGHD across healthcare organizations and providers.
Ethical Considerations
As healthcare organizations continue to leverage PGHD, it is essential to address several ethical considerations to protect patient privacy, autonomy, and rights. Some of the key ethical considerations include:
Informed Consent
Patients must provide informed consent before their data is collected, shared, or used for research purposes. Healthcare providers and organizations should clearly communicate the purpose, scope, and potential risks and benefits of collecting and using PGHD to ensure patients can make informed decisions about their participation.
Data Ownership and Control
Patients should have ownership and control over their PGHD, including the ability to access, manage, and share their data as they see fit. Healthcare organizations should implement transparent policies and procedures for data ownership and control, respecting patients’ rights to privacy and autonomy.
Data Security and Confidentiality
Ensuring the security and confidentiality of PGHD is paramount to protect sensitive patient information from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure. Healthcare organizations must implement robust data protection measures, such as encryption, access controls, and secure storage solutions, to safeguard PGHD and comply with relevant data privacy regulations.
How Siam Computing Can Help
Patient-Generated Health Data (PGHD) holds significant promise for revolutionizing healthcare by empowering patients, enhancing clinical decision-making, and supporting personalized medicine initiatives. Despite the challenges and ethical considerations associated with collecting and using PGHD, ongoing advancements in technology, AI, and data analytics are poised to drive the adoption and integration of PGHD in healthcare.
At Siam Computing, we specialize in building secure digital healthcare solutions and patient experience platforms tailored to the unique needs of healthtech startups, hospitals, and other healthcare institutions. Our expertise in developing custom healthcare solutions enables us to effectively leverage PGHD to improve patient care and outcomes.
If you are interested in leveraging Patient-Generated Health Data to enhance your healthcare digital products and platforms, contact our product strategists today. Learn how our digital healthcare experts can help you develop custom solutions that effectively collect, analyze, and utilize PGHD to improve patient care, engagement, and outcomes.