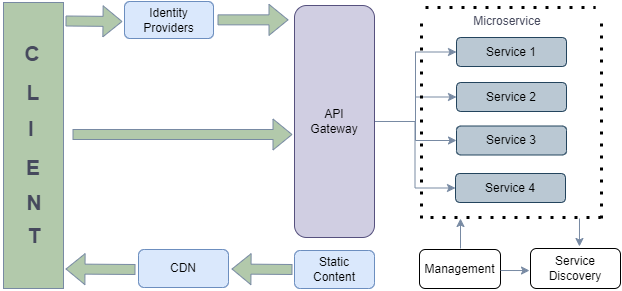
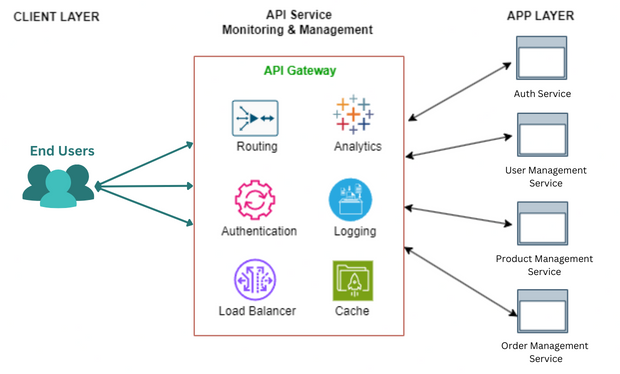
In today’s dynamic e-commerce landscape, efficiency is key to success. For this reason, developers often turn to microservices architecture for its adaptability in this rapidly evolving scenario. However, managing different services in the microservices architecture brings its own set of challenges for developers to attain streamlined coordination.
This article explores the role of API Gateways in addressing these challenges and optimizing e-commerce operations. From simplifying user access to enhancing security and performance, API Gateways play a pivotal role in the ever-evolving world of microservices.
Microservices and Their Challenges
As a web developer working on an e-commerce platform encompassing four core services (Auth Service, User management, Product Management and Order management), I initially deployed these services across separate domains. Yet, as the platform expanded, managing and coordinating these components posed challenges.
With the platform’s growth, certain services encountered prolonged response times, prompting me to explore the potential of an API Gateway. This versatile tool not only consolidates services under a unified domain but also orchestrates load balancing. In this article, we will delve into the developer’s viewpoint on how API Gateways can streamline operations, enhance service response times, and confer a competitive advantage in the ever-evolving realm of e-commerce.
Let us look at microservices in greater detail.
Microservices Architecture
Microservices architecture is a software development approach that structures an application as a collection of small, loosely coupled services. Each service is responsible for a specific piece of functionality and operates independently. Here are some key aspects of microservices:
Service Independence
Each microservice is an independent unit of deployment and operation. It can be developed, tested, deployed, and scaled separately from other services. This independence allows for agility in development, as changes in one service do not impact the entire application.
API-Based Communication
Microservices communicate with each other through well-defined APIs, typically over HTTP or other lightweight protocols. This approach enables services to work together, even if they are written in different programming languages or use different technology stacks.
Scalability
Microservices can be scaled individually based on their specific resource needs. This means that services experiencing heavy traffic can be scaled up while less-used services can remain at their current scale. Scalability is a crucial aspect of microservices, particularly in scenarios like e-commerce applications, where demand fluctuates rapidly.
Data Management
Each microservice manages its own data store. This may involve using different types of databases or storage systems. Data consistency is maintained through careful design and the use of distributed transactions or event-driven mechanisms.
Fault Isolation
Microservices are designed to be fault-tolerant. If one service encounters an issue or failure, it should not bring down the entire system. Instead, the application should gracefully degrade, and other services should continue to function.
Continuous Delivery
Microservices are often developed, tested, and deployed using DevOps and continuous integration/continuous delivery (CI/CD) practices. This enables rapid updates and new feature releases.
Flexibility
Microservices are well-suited for applications that require flexibility in choosing the technology stack for each service. Different services can use the programming languages, databases, and tools that best fit their specific requirements.
Decomposition
The process of breaking down a monolithic application into microservices is known as decomposition. It involves identifying the boundaries of each service, which can be based on business capabilities or domain-driven design principles. This decomposition process is crucial for ensuring that microservices are well-structured and maintainable.
Let us understand microservices through the following use cases.
Microservices Use Cases
Microservices are commonly used in a wide range of applications, including e-commerce platforms, social media networks, banking etc.,. They are particularly valuable in situations where scalability, rapid development, and resilience are critical.
E-commerce Platforms
E-commerce platforms handle a vast array of services, including product catalog, user profiles, payment processing, and order management. Microservices architecture allows these platforms to scale individual components based on demand, ensuring a seamless shopping experience for users. API Gateways simplify user access and enhance performance, crucial for handling the high traffic and varying workloads of e-commerce.
Social Media Networks
Social media platforms rely on a multitude of features, such as user profiles, timelines, messaging, and content storage. Microservices enable these platforms to evolve rapidly by developing and deploying new features independently. API Gateways play a vital role in routing requests, handling security, and providing analytics to enhance user engagement.
Banking Applications
In the highly regulated and data-sensitive environment of banking, microservices offer flexibility and maintainability. Banking applications often consist of services for account management, transactions, and security. API Gateways secure sensitive transactions, offer centralized management, and ensure that customer data remains safe.
Navigating Challenges in E-commerce Microservices
Microservices, despite their manifold advantages, bring a series of challenges before developers and operations teams. Here are some of them:
Complexity Management
The proliferation of services amplifies complexities in their orchestration, data consistency, and inter-service communication, demanding adept coordination from development and operations units.
Ensuring Data Consistency
As each microservice governs its own data, ensuring coherence across the application becomes very challenging, often necessitating distributed transaction mechanisms or event-driven solutions for preserving data integrity.
Vigilant Health Monitoring
The vigilant monitoring of each microservice’s health is critical to the system’s maintenance. This necessitates robust alerting systems and monitoring mechanisms to detect and respond promptly to potential features.
Safeguarding Security
Microservices demand meticulous attention to security, encompassing authentication, authorization, and data protection across multiple layers. The complex choreography of security measures while maintaining a coherent posture makes for an additional layer of complexity.
Streamlining Documentation
The laborious task of documenting myriad APIs across diverse microservices is a fundamental challenge. Clear and consistent documentation remains indispensable for developers to effectively engage with and comprehend these services.
Role of API Gateways in E-commerce
API Gateways exercise immense power by consolidating essential services, transforming a disparate array of functionalities authentication, user management, product management, and order management into a cohesive unit under a unified domain. This strategic alignment augments the platform’s efficacy and coherence, simplifying processes and fortifying the e-commerce applications overall effectiveness.
Bringing Four Services Under One Domain
Picture a scenario where these critical services Auth Service, User management, Product Management and Order management are initially spread across four separate domains. This setup can lead to a maze of complexities in terms of development, maintenance, and user experience. The challenge is clear: how can one consolidate these services under one unified domain, achieving seamless interaction and a holistic application?
The API Gateway Solution
This is where the API gateway enters the scene as a strategic ally. API gateways act as the central traffic controllers, directing incoming client requests to the appropriate service, irrespective of the domain. By doing so, they create a single entry point to the application, streamlining the user experience and unifying the services under one domain.
Simplifying User Access
API gateways simplify client access to the application. Clients interact with a single entry point, eliminating the need to navigate multiple domains. This unified interface enhances the user experience, making it easier for clients to communicate with the services. In the dynamic world of online retail, where speed and accessibility are paramount, this simplicity provides a competitive advantage.
Optimizing Security and Performance
Beyond simplifying user access, API gateways enhance security and performance. They manage authentication and authorization, ensuring that only authorized requests reach the respective microservices. This layer of security protects sensitive data and functionalities. Moreover, the gateways provide load balancing, evenly distributing traffic across microservices, enhancing scalability and system reliability.
Advantages of Integrating API Gateways in E-commerce Microservices
In addition to mitigating the above mentioned challenges, API Gateways present a host of advantages in the realm of e-commerce microservices:
Centralized Management
API Gateways serve as centralized control points, streamlining incoming and outgoing requests while facilitating unified management of the entire microservices ecosystem. Tasks such as logging, monitoring, and error handling find simplification through this centralized control.
Version Control
The dynamic nature of e-commerce applications necessitates constant evolution. API Gateways enable versioning of APIs, ensuring backward compatibility for existing clients while allowing newer clients to leverage the latest enhancements, an indispensable feature in the ever-evolving e-commerce landscape.
Caching and Performance Optimization
API Gateways implement caching mechanisms that store frequently accessed data, alleviating the load on microservices, expediting response times, and conserving resources—an invaluable asset in e-commerce scenarios where real-time data access is critical.
Scalability and Error Handling
Crucial to e-commerce, API Gateways enable intelligent distribution of traffic across multiple microservice instances, ensuring scalability to accommodate surges in demand. Additionally, their role in error interception and response bolsters the platform’s resilience against service disruptions.
Insights and Documentation Simplification
API Gateways offer profound insights into client interaction patterns, performance metrics, and behavioral analytics, aiding informed decision-making. Furthermore, built-in tools for documentation simplify API understanding for both internal and external stakeholders.
Final Thoughts
Within the domain of an e-commerce application, API gateways play a pivotal role in consolidating four crucial services, streamlining user interactions, fortifying security measures, and bolstering operational performance. This unified experience within application not only ensures efficiency but also positions itself as a competitive advantage within the dynamic modern business milieu.
As you navigate the complexities of integrating API gateways into an e-commerce application, recognize their pivotal role in establishing a cohesive service domain. They are the cornerstone for simplicity and efficiency, propelling the e-commerce application to unprecedented levels. Moreover, the integration of microservices architecture empowers applications with adaptability, scalability, and resilience in a continually evolving market landscape.
About the author

Jegan Rajaiya is a tech lead at Siam Computing, with over 8 years of experience in web development. He is an expert in Python and PHP, with remarkable skills in frameworks such as Django and Laravel. He is passionate about leveraging cutting-edge technologies to craft reliable and user-friendly solutions. With a knack for problem-solving, he thrives on addressing and simplifying complex challenges. Alongside this passion, he is actively mentoring young developers and fostering a culture of growth within his team.