Chronic diseases pose a serious challenge in India, accounting for a large proportion of the country’s health burden. Conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular diseases are on the rise due to lifestyle changes, urbanization, and ageing populations.
These diseases not only affect the quality of life but also impose a heavy financial burden on individuals and the healthcare system, especially those belonging to low-income families. Chronic disease management in India requires a robust approach, focusing on prevention, early detection, and continuous monitoring.
Importance of Chronic Disease Management in India
- Prevalence: According to National Institute of Health, about 21% of the elderly in India reportedly have at least one chronic disease. Seventeen percent elderly in rural areas and 29% in urban areas suffer from a chronic disease. Hypertension and diabetes account for about 68% of all chronic diseases. Additionally, rapid urbanization, changing lifestyles, and dietary challenges also contribute significantly to the prevalence of NCDs in India.
- Economic Impact: The management of chronic diseases drains healthcare resources, contributing to increased out-of-pocket expenses for Indian families.
- Health System Challenges: Limited access to healthcare services, especially in rural areas, further exacerbates the problem.
- These factors significantly highlight the challenges of chronic diseases in India and the importance of healthcare portals in bridging these gaps.
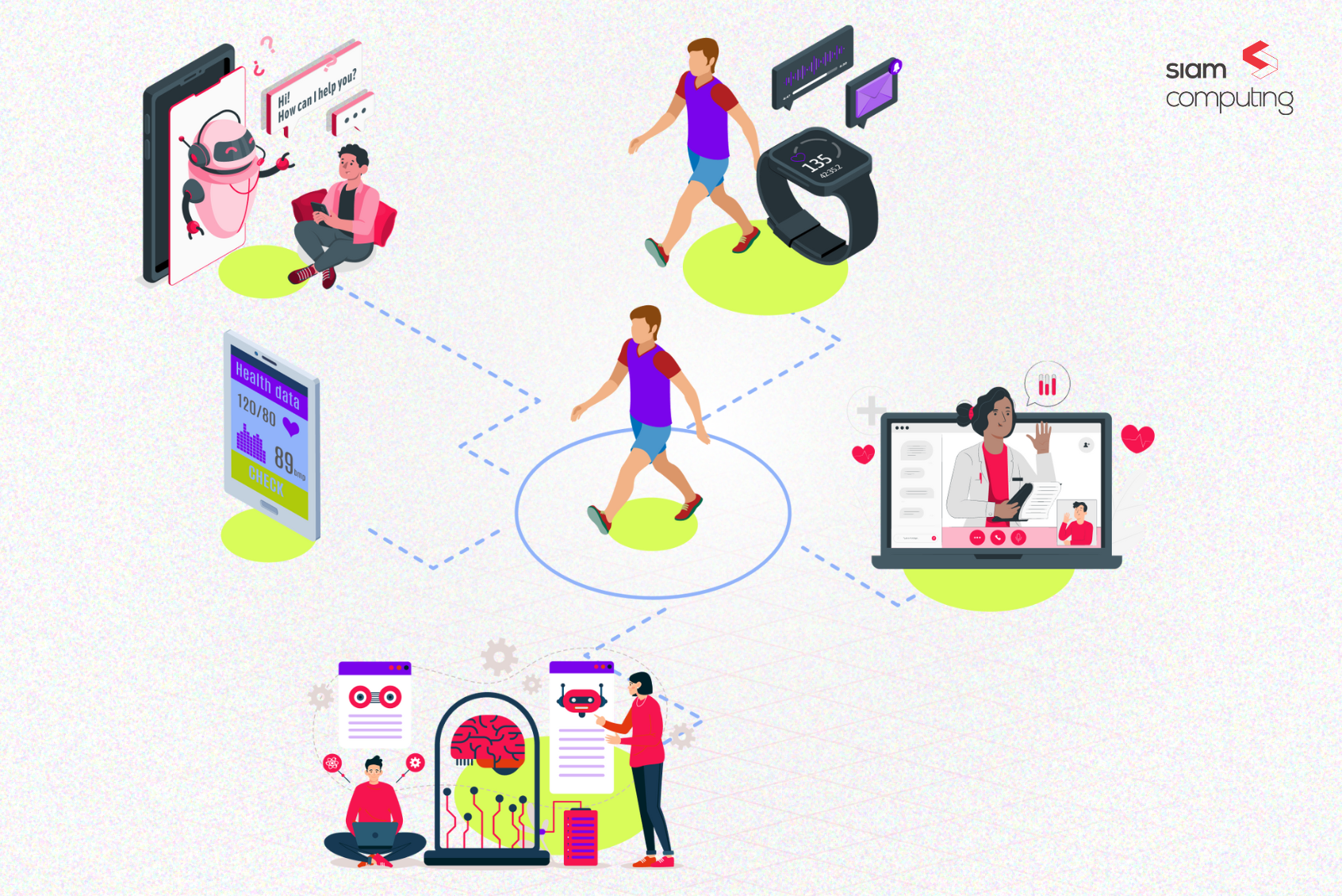
Data Collection for Health Portals
Data is collected and analyzed on a wide range of patient information to identify high-risk individuals, predict potential complications, and tailor interventions for improved outcomes. This data can come from various sources:
Demographics:
Health portals collect basic details such as age, gender, and family medical history. These data points are foundational for creating patient profiles and tailoring health recommendations. For instance, a patient’s age and family history can indicate the likelihood of genetic conditions like diabetes or hypertension, influencing their personalized care plans.
Clinical Data:
This includes vital health metrics such as blood pressure, glucose levels, cholesterol levels, and diagnostic test results. Such data is collected during medical consultations, lab tests, or through wearable devices. Clinical data helps monitor disease progression, detect early warning signs, and adjust treatment protocols as needed.
Behavioral Data:
Health portals track lifestyle-related data such as exercise routines, dietary habits, smoking, alcohol consumption, and sleep patterns. Behavioral data provides insight into a patient’s daily habits, allowing for more effective preventive measures or lifestyle modifications. For instance, irregular sleep patterns prompt interventions for stress management or sleep hygiene.
Device-Generated Data:
Wearables like smartwatches, fitness trackers, and glucometers contribute continuous, real-time health data to the portal. Metrics like heart rate variability, step counts, and glucometers help identify immediate risks or patterns in health, enabling timely interventions.
Source of Data collected for Health portals
There are various contributors to health portal data. These sources are:
1. Patient-Provided Data
Patients play an active role in contributing their health information via:
- Manual Inputs: Through health portals or apps, patients record their symptoms, lifestyle habits, progress, and health goals. For instance, they might log daily blood sugar levels, weight, or dietary intake.
- Connected Devices: Wearable technologies like fitness trackers, glucometers, and smartwatches automatically transmit data such as heart rate, oxygen saturation, or activity levels to the portal.
2. Healthcare Providers
Clinicians and diagnostic labs contribute clinical data, including:
- Medical Consultation Records: Information from doctor visits, including diagnoses, prescriptions, and treatment plans.
- Diagnostic Tests: Lab results such as blood reports, imaging scans, or pathology results are uploaded to patient profiles for seamless access.
- Interoperability with Hospital Systems: Many portals integrate with hospital information systems (HIS) to update patient records automatically.
3. Wearable Devices
Advanced health trackers and medical-grade devices continuously monitor and transmit real-time health metrics, including:
- Heart Rate and Blood Pressure for managing cardiovascular conditions.
- Oxygen Saturation (SpO2) is used during conditions like COVID-19 or respiratory disorders.
- Glucose Levels that are critical for diabetes management.
4. Patient Surveys and Questionnaires
Patients often fill in surveys or feedback forms via the portal to provide:
- Symptom Tracking: This includes data filled out by patients about their symptoms like pain, fatigue, and more.
- Lifestyle Information: Details about sleep patterns, stress levels, or dietary habits.
What Happens to the Data in Health Portals?
After patient data is collected through various channels, it is processed through several key stages to ensure it serves its intended purpose of delivering meaningful insights, enabling personalized care, and empowering patients.
Storage and Securing the Data
Patient data is securely stored in cloud-based systems or dedicated servers designed to:
- Ensure Accessibility: Authorized patients and healthcare providers can access the data anytime, anywhere, improving the continuity of care.
- Protect Privacy: Data storage systems comply with global and local data protection laws, such as GDPR or India’s Personal Data Protection Bill. This ensures that sensitive health information remains confidential.
Integration: Unifying Disparate Sources
Health portals leverage Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) to aggregate data from:
- Diagnostic Labs: Lab test results are automatically updated in patient profiles.
- Pharmacies: Information on prescriptions and refills is integrated for medication tracking.
- Wearables and IoT Devices: Devices like glucometers and fitness trackers continuously feed real-time metrics into the portal.
Data Management Portals and Standardised Formats:
Data storage and processing must also ensure accessibility for various provider-payer systems and centralized agencies to transmit and decipher the data in real-time. A few initiatives and frameworks that provide broader data integration capabilities are:
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs): Centrally managed records offer a unified view of a patient’s medical history, accessible to both patients and providers. There are various kinds and formats for EHR records and data.
- Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM): ABDM in India ensures interoperability across healthcare systems in India by linking patient data with unique health IDs. It facilitates access to comprehensive health records, regardless of where care is provided.
Analysis: Turning Data Into Actionable Insights
Collected data undergoes advanced processing using algorithms and machine learning techniques to derive insights such as:
- Trend Identification: Continuous monitoring detects patterns, such as a patient’s rising blood sugar levels, prompting timely interventions.
- Adherence Tracking: Analysis of medication schedules highlights lapses, helping doctors recommend corrective actions.
- Risk Assessment: Predictive models assess the likelihood of complications, allowing preventive measures.
Benefits of Health Portals in Chronic Disease Management
- Improved Access to Medical Records: Health portals allow patients to view their medical history, lab results, and treatment plans in real-time. This transparency helps patients stay informed and reduces their dependency on physical document management.
- Encouraging Active Participation: Many portals offer tools for patients to track symptoms, monitor their progress, and set health goals. This proactive engagement has been linked to better health outcomes as patients are more involved in their care plans.
- Time Efficiency: Patients can use health portals to book appointments, request prescriptions, and access lab results online, reducing the need for in-person visits and saving time for both patients and providers.
- Medication Adherence: Health portals provide automated reminders for prescription refills and medical appointments. This feature ensures that patients maintain consistency in their medication intake, improving overall treatment outcomes.
- Better Monitoring of Complex Conditions: Health portals integrate data from various care providers, offering a consolidated view of patient health. This is particularly useful for patients managing multiple chronic conditions, as it streamlines care coordination and reduces errors.
- Improved communication with Providers: Secure messaging systems in portals enable patients to reach out to healthcare providers quickly. This feature enhances coordination, allowing providers to address patient concerns promptly and improve continuity of care.
Revolutionizing Indian healthcare systems with Health Portals
As India heads forward in its journey toward universal healthcare access, the integration of technology in chronic disease management is no longer optional; and it is now imperative. Digital health solutions, such as health portals, telemedicine, and AI-driven tools, have the power to bridge long-standing gaps in accessibility and quality of care. The future of healthcare in India depends on our ability to ensure that these solutions are designed for inclusivity, affordability, and scalability.
The days of pondering are over, and it is time for healthcare pioneers and policymakers to act. By collaborating to address barriers such as digital literacy, cost, and infrastructure challenges, we can create a healthcare system that leaves no one behind. The greatest opportunities lie in serving underserved populations, rural communities, the elderly, low-income families, and those with chronic illnesses. It is now time to ensure that technology no longer remains limited to the educated. It is time technology becomes a force for equity.
At Siam Computing, we specialize in building innovative, user-friendly, and scalable digital health solutions that address the unique needs of diverse populations. Whether you’re a healthcare provider looking to implement health portals or a startup aiming to create patient-centric platforms, our product strategy and development expertise can help you bring your vision to life.
The potential to make a difference is immense. Let’s work together to transform India’s healthcare landscape. Contact our team today to start building solutions that matter and bring us together.